امتحان نهاية الفصل الدراسي الثاني )يونية ) ٢٠١٥. Computer Architectures (CS x35) معماريات الحاسب x35) (CS. ii. if (g >= h) g = g + 1; else h = h 1;
|
|
|
- Molly Welch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alexandria University جامعة اإلسكندرية Faculty of Engineering كلية الهندسة Electrical Engineering Department قسم الهندسة الكهربية Final Exam, June 2015 امتحان نهاية الفصل الدراسي الثاني )يونية ) ٢٠١٥ Course Title and Code Number: اسم المقرر والرقم الكودي له: Computer Architectures (CS x35) معماريات الحاسب x35) (CS Fourth Year (Communications and Electronics) السنة الدراسية الرابعة )اتصاالت و الكترونيات ) Time Allowed: 3 hours الزمن: ٣ ساعات Attempt all questions: (75 marks) Question 1: (19 marks) a) Implement the following high-level code segments using the slt instruction. Assume the integer variables g and h are in registers $s0 and $s1, respectively. (MIPS Instruction Set Summary is given in page 8) i. if (g > h) g = g + h; else g = g h; ii. if (g >= h) g = g + 1; else h = h 1; iii. if (g <= h) g = 0; else h = 0; b) Write a MIPS assembly program equivalent to the following pseudo-instructions. If necessary, you can use register $t0 to memorize intermediary values. No other register can be used. i. add ($s0),$s1,($s2) #mem[$s0]=$s1+mem[$s2] This MIPS instruction does not exist, because it uses an addressing mode not supported by RISC processors. ii. SWAP $s0 # bits <-> bits 15-0 This instruction allows us to swap the 16 most significant bits with the 16 least significant ones of a 32-bit word. iii. PUSH $s0 This instruction is not a MIPS instruction either. It decrements the stack pointer (SP), then saves $s0 at this address. c) Consider the following high-level function. i. Translate the high-level function f into MIPS assembly language. Pay particular attention to properly saving and restoring registers across function calls and using the MIPS preserved register conventions. Clearly comment your code. You can use the MIPS mul instruction. The function starts at instruction address 0x Keep local variable b in $s0. ii. Step through your function from part (a) by hand for the case of f(2,4). Draw a picture showing stack memory contents. Write the register name and data value stored at each location in the stack and keep track of the stack pointer value ($sp). Clearly mark each Page 1 of 8
2 stack frame. You might also find it useful to keep track of the values in $a0, $a1, $v0, and $s0 throughout execution. Assume that when f is called, $s0 = 0xABCD and $ra = 0x What is the final value of $v0? Question 2 (24 marks) a) Modify the multicycle MIPS processor to implement one of the following instructions. Indicate the changes to the datapath and name any new control signals. Show the changes to the controller FSM and describe any other changes that are required. (Add your modifications to Figure 1 and 2 and attach the paper containing pages 5 and 6 to your answer paper). i. xori ii. jr iii. bne iv. lb b) What is the CPI of the redesigned multicycle MIPS? Use delay Table 1 and the following and instruction mix: The SPECINT2000 benchmark consists of approximately 25% loads, 10% stores, 11% branches, 2% jumps, and 52% R-type instructions. c) Explain with examples two data and control hazards in a five-stage MIPS pipelined processor. Show how to handle these hazards at both compileand run-time. (The Pipelined MIPS processor architecture is shown in Figure 3) Table 1: Delay of processor elements d) Suppose the MIPS pipelined processor is divided into 10 stages of 400 ps each, including sequencing overhead. Assume the instruction mix of the SPECINT2000 benchmark. Also assume that 50% of the loads are immediately followed by an instruction that uses the result, requiring six stalls, and that 30% of the branches are mispredicted. The target address of a branch or jump instruction is not computed until the end of the second stage. Calculate the average CPI and execution time of computing 100 billion instructions from the SPECINT2000 benchmark for this 10-stage pipelined processor. Question 3: (18 marks) a) You are building an instruction cache for a MIPS processor. It has a total capacity of 4C = 2 c+2 bytes. It is N = 2 n -way set associative (N 8), with a block size of b = 2 b bytes (b 8). Give your answers to the following questions in terms of these parameters. i. Which bits of the address are used to select a word within a block? ii. Which bits of the address are used to select the set within the cache? Page 2 of 8
3 iii. iv. How many bits are in each tag? How many tag bits are in the entire cache? b) Consider a cache with the following parameters: N (associativity) = 2, b (block size) = 2 words, W (word size) = 32 bits, C (cache size) = 32 K words, A (address size) = 32 bits. You need to consider only word addresses. i. Show the tag, set, block offset, and byte offset bits of the address. State how many bits are needed for each field? ii. What is the size of all the cache tags in bits? iii. Suppose each cache block also has a valid bit (V) and a dirty bit (D). What is the size of each cache set, including data, tag, and status bits? iv. Design the cache using the building blocks in Figure 4 and a small number of two-input logic gates. The cache design must include tag storage, data storage, address comparison, data output selection, and any other parts you feel are relevant. Note that the multiplexer and comparator blocks may be any size (n or p bits wide, respectively), but the SRAM blocks must be 16K 4 bits. Be sure to include a neatly labeled block diagram. You need only design the cache for reads. Figure 4: Building blocks c) Consider a virtual memory system that can address a total of 2 32 bytes. You have unlimited hard drive space, but are limited to only 8 MB of semiconductor (physical) memory. Assume that virtual and physical pages are each 4 KB in size. i. How many bits is the physical address, virtual and physical page numbers? ii. What is the maximum number of virtual pages in the system? iii. How many physical pages are in the system? iv. Suppose that you come up with a direct mapped scheme that maps virtual pages to physical pages. The mapping uses the least significant bits of the virtual page number to determine the physical page number. How many virtual pages are mapped to each physical page? Why is this direct mapping a bad plan? v. Clearly, a more flexible and dynamic scheme for translating virtual addresses into physical addresses is required than the one described in part (iv). Suppose you use a page table to store mappings (translations from virtual page number to physical page number). How many page table entries will the page table contain? vi. Sketch the layout of the page table. What is the total size of the page table in bytes? Page 3 of 8
4 Question 4: (14 marks) a) Computationally efficient approximations for the magnitude function are presented in Table 3. Give three alternative architectures that implement the algorithm and compare them in terms of datapath resources, cycles per data item, longest path, and control overhead. Assume input data remain valid as long as you need them, but plan for a registered output. Begin by drawing the DDG. Table 3: Approximations for computing magnitudes a) Arithmetic mean x and standard deviation σ are defined as Assume samples x n arrive sequentially one at a time. More specifically, each clock cycle sees a new w-bit data item appear. Find a dedicated architecture that computes x and σ 2 after N clock cycles and where N is some integer power of two, say 32. Definitions in the above equations suggest one needs to store up to N 1 past values of x. Can you make do with less? What mathematical properties do you call on? What is the impact on datapath word width? Good Luck Dr. Mohammed Morsy Page 4 of 8
5 Answer Question 2(a) in this page and attach (staple) it to the answer paper Do not write your personal data (name or seat number) on this paper Figure 1: MIPS multicycle processor Page 5 of 8
6 Answer Question 2(a) in this page and attach (staple) it to the answer paper Do not write your personal data (name or seat number) on this paper Figure 2: MIPS multicycle processor FSM Page 6 of 8
7 Figure 3: Pipelined MIPS The MIPS Processor Instruction Format Page 7 of 8
8 Page 8 of 8
Alexandria University
 Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 2 1. Modify the single-cycle MIPS processor to implement one of the following instructions.
Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 2 1. Modify the single-cycle MIPS processor to implement one of the following instructions.
Alexandria University
 Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 3 1. A cache has the following parameters: b, block size given in numbers of words;
Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 3 1. A cache has the following parameters: b, block size given in numbers of words;
Alexandria University
 Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 1: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture Exercises 1-16 from the reference book: Digital
Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Division of Communications & Electronics CC322 Computer Architecture Sheet 1: MIPS Instruction Set Architecture Exercises 1-16 from the reference book: Digital
OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES. NO COMPUTERS, OR SOLVING PROBLEMS DIRECTLY USING CALCULATORS.
 CS/ECE472 Midterm #2 Fall 2008 NAME: Student ID#: OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES. NO COMPUTERS, OR SOLVING PROBLEMS DIRECTLY USING CALCULATORS. Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will
CS/ECE472 Midterm #2 Fall 2008 NAME: Student ID#: OPEN BOOK, OPEN NOTES. NO COMPUTERS, OR SOLVING PROBLEMS DIRECTLY USING CALCULATORS. Your signature is your promise that you have not cheated and will
Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3
 Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
Name: Computer Architecture CS372 Exam 3 This exam has 7 pages. Please make sure you have all of them. Write your name on this page and initials on every other page now. You may only use the green card
CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2001
 CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2 Name: This exam has 4 pages, including this cover. There are six questions, worth a total of 5 points. You have 3 hours. Budget your time! Write clearly and show your work. State
CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2 Name: This exam has 4 pages, including this cover. There are six questions, worth a total of 5 points. You have 3 hours. Budget your time! Write clearly and show your work. State
CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2001
 CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2 Name: Spiderman This exam has 4 pages, including this cover. There are six questions, worth a total of 5 points. You have 3 hours. Budget your time! Write clearly and show your
CS232 Final Exam May 5, 2 Name: Spiderman This exam has 4 pages, including this cover. There are six questions, worth a total of 5 points. You have 3 hours. Budget your time! Write clearly and show your
CS/COE1541: Introduction to Computer Architecture
 CS/COE1541: Introduction to Computer Architecture Dept. of Computer Science University of Pittsburgh http://www.cs.pitt.edu/~melhem/courses/1541p/index.html 1 Computer Architecture? Application pull Operating
CS/COE1541: Introduction to Computer Architecture Dept. of Computer Science University of Pittsburgh http://www.cs.pitt.edu/~melhem/courses/1541p/index.html 1 Computer Architecture? Application pull Operating
Computer Architecture (CC 322) معماريات الحاسب 322) (CC
 Alexandria University جامعة اإلسكندرية Faculty of Engineering كلية الهندسة Computers and Communications Department قسم هندسة الحاسبات واالتصاالت Spring Final Exam, June 2016 امتحان نهاية الفصل الدراسي
Alexandria University جامعة اإلسكندرية Faculty of Engineering كلية الهندسة Computers and Communications Department قسم هندسة الحاسبات واالتصاالت Spring Final Exam, June 2016 امتحان نهاية الفصل الدراسي
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination
 THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
THE HONG KONG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Computer Organization (COMP 2611) Spring Semester, 2014 Final Examination May 23, 2014 Name: Email: Student ID: Lab Section Number: Instructions: 1. This
CS 230 Practice Final Exam & Actual Take-home Question. Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts)
 Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts) 1. Assume that assembly code for the following variable definitions has already been generated (and initialization of A and length). int powerof2; /* powerof2
Part I: Assembly and Machine Languages (22 pts) 1. Assume that assembly code for the following variable definitions has already been generated (and initialization of A and length). int powerof2; /* powerof2
CSE 378 Final Exam 3/14/11 Sample Solution
 Name There are 8 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions don t miss the short questions at the end. Keep your answers brief and to the point. Copies
Name There are 8 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions don t miss the short questions at the end. Keep your answers brief and to the point. Copies
ENGN 2910A Homework 03 (140 points) Due Date: Oct 3rd 2013
 ENGN 2910A Homework 03 (140 points) Due Date: Oct 3rd 2013 Professor: Sherief Reda School of Engineering, Brown University 1. [from Debois et al. 30 points] Consider the non-pipelined implementation of
ENGN 2910A Homework 03 (140 points) Due Date: Oct 3rd 2013 Professor: Sherief Reda School of Engineering, Brown University 1. [from Debois et al. 30 points] Consider the non-pipelined implementation of
ISA Instruction Operation
 This exam has 6 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
This exam has 6 problems. Make sure you have a complete exam before you begin. Write your name on every page in case pages become separated during grading. You will have three hours to complete this exam.
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 13, 2000
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have until 11:00AM. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. Floating Point Representation / MIPS Assembly Language
This exam is open book and open notes. You have until 11:00AM. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. Floating Point Representation / MIPS Assembly Language
Chapter 2A Instructions: Language of the Computer
 Chapter 2A Instructions: Language of the Computer Copyright 2009 Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Instruction Set The repertoire of instructions of a computer Different computers have different instruction
Chapter 2A Instructions: Language of the Computer Copyright 2009 Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Instruction Set The repertoire of instructions of a computer Different computers have different instruction
CSCE 212: FINAL EXAM Spring 2009
 CSCE 212: FINAL EXAM Spring 2009 Name (please print): Total points: /120 Instructions This is a CLOSED BOOK and CLOSED NOTES exam. However, you may use calculators, scratch paper, and the green MIPS reference
CSCE 212: FINAL EXAM Spring 2009 Name (please print): Total points: /120 Instructions This is a CLOSED BOOK and CLOSED NOTES exam. However, you may use calculators, scratch paper, and the green MIPS reference
ECE550 PRACTICE Final
 ECE550 PRACTICE Final This is a full length practice midterm exam. If you want to take it at exam pace, give yourself 175 minutes to take the entire test. Just like the real exam, each question has a point
ECE550 PRACTICE Final This is a full length practice midterm exam. If you want to take it at exam pace, give yourself 175 minutes to take the entire test. Just like the real exam, each question has a point
Lab 4 Prelab: MIPS Function Calls
 Lab 4 Prelab: MIPS Function Calls Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of
Lab 4 Prelab: MIPS Function Calls Name: Sign the following statement: On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work 1 Objective The main objective of
c. What are the machine cycle times (in nanoseconds) of the non-pipelined and the pipelined implementations?
 Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
Brown University School of Engineering ENGN 164 Design of Computing Systems Professor Sherief Reda Homework 07. 140 points. Due Date: Monday May 12th in B&H 349 1. [30 points] Consider the non-pipelined
ECE 2035 Programming HW/SW Systems Fall problems, 7 pages Exam Two 23 October 2013
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Winter 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION Auxiliary Gymnasium Tuesday, April 18 7:00pm to 10:00pm
 University of Calgary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ENCM 369: Computer Organization Lecture Instructor for L01 and L02: Dr. S. A. Norman Winter 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION Auxiliary Gymnasium
University of Calgary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ENCM 369: Computer Organization Lecture Instructor for L01 and L02: Dr. S. A. Norman Winter 2006 FINAL EXAMINATION Auxiliary Gymnasium
MIPS ISA and MIPS Assembly. CS301 Prof. Szajda
 MIPS ISA and MIPS Assembly CS301 Prof. Szajda Administrative HW #2 due Wednesday (9/11) at 5pm Lab #2 due Friday (9/13) 1:30pm Read Appendix B5, B6, B.9 and Chapter 2.5-2.9 (if you have not already done
MIPS ISA and MIPS Assembly CS301 Prof. Szajda Administrative HW #2 due Wednesday (9/11) at 5pm Lab #2 due Friday (9/13) 1:30pm Read Appendix B5, B6, B.9 and Chapter 2.5-2.9 (if you have not already done
CSEE W3827 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Homework Assignment 5 Solutions
 CSEE W3827 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Homework Assignment 5 Solutions Profs. Stephen A. Edwards & Martha Kim Columbia University Due December 10th, 2012 at 5:00 PM Turn in at CSB 469. Write your
CSEE W3827 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Homework Assignment 5 Solutions Profs. Stephen A. Edwards & Martha Kim Columbia University Due December 10th, 2012 at 5:00 PM Turn in at CSB 469. Write your
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 14, This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours.
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-5 refer to the following: We wish to add a new R-Format instruction to the MIPS Instruction Set Architecture called l_inc (load and increment).
This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-5 refer to the following: We wish to add a new R-Format instruction to the MIPS Instruction Set Architecture called l_inc (load and increment).
SOLUTION. Midterm #1 February 26th, 2018 Professor Krste Asanovic Name:
 SOLUTION Notes: CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS 252 Graduate Computer Architecture Midterm #1 February 26th, 2018 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: I am taking CS152 / CS252 This is a closed
SOLUTION Notes: CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering CS 252 Graduate Computer Architecture Midterm #1 February 26th, 2018 Professor Krste Asanovic Name: I am taking CS152 / CS252 This is a closed
Chapter 2: Instructions:
 Chapter 2: Instructions: Language of the Computer Computer Architecture CS-3511-2 1 Instructions: To command a computer s hardware you must speak it s language The computer s language is called instruction
Chapter 2: Instructions: Language of the Computer Computer Architecture CS-3511-2 1 Instructions: To command a computer s hardware you must speak it s language The computer s language is called instruction
CS 352H Computer Systems Architecture Exam #1 - Prof. Keckler October 11, 2007
 CS 352H Computer Systems Architecture Exam #1 - Prof. Keckler October 11, 2007 Name: Solutions (please print) 1-3. 11 points 4. 7 points 5. 7 points 6. 20 points 7. 30 points 8. 25 points Total (105 pts):
CS 352H Computer Systems Architecture Exam #1 - Prof. Keckler October 11, 2007 Name: Solutions (please print) 1-3. 11 points 4. 7 points 5. 7 points 6. 20 points 7. 30 points 8. 25 points Total (105 pts):
Chapter 2. Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
 Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) MIPS arithmetic Design Principle: simplicity favors regularity. Why? Of course this complicates some things... C code: A = B + C + D; E = F - A; MIPS code:
Chapter 2 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) MIPS arithmetic Design Principle: simplicity favors regularity. Why? Of course this complicates some things... C code: A = B + C + D; E = F - A; MIPS code:
Instructions: MIPS arithmetic. MIPS arithmetic. Chapter 3 : MIPS Downloaded from:
 Instructions: Chapter 3 : MIPS Downloaded from: http://www.cs.umr.edu/~bsiever/cs234/ Language of the Machine More primitive than higher level languages e.g., no sophisticated control flow Very restrictive
Instructions: Chapter 3 : MIPS Downloaded from: http://www.cs.umr.edu/~bsiever/cs234/ Language of the Machine More primitive than higher level languages e.g., no sophisticated control flow Very restrictive
Write only as much as necessary. Be brief!
 1 CIS371 Computer Organization and Design Midterm Exam Prof. Martin Thursday, March 15th, 2012 This exam is an individual-work exam. Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached
1 CIS371 Computer Organization and Design Midterm Exam Prof. Martin Thursday, March 15th, 2012 This exam is an individual-work exam. Write your answers on these pages. Additional pages may be attached
EE 361 University of Hawaii Fall
 C functions Road Map Computation flow Implementation using MIPS instructions Useful new instructions Addressing modes Stack data structure 1 EE 361 University of Hawaii Implementation of C functions and
C functions Road Map Computation flow Implementation using MIPS instructions Useful new instructions Addressing modes Stack data structure 1 EE 361 University of Hawaii Implementation of C functions and
Computer Architecture. Chapter 2-2. Instructions: Language of the Computer
 Computer Architecture Chapter 2-2 Instructions: Language of the Computer 1 Procedures A major program structuring mechanism Calling & returning from a procedure requires a protocol. The protocol is a sequence
Computer Architecture Chapter 2-2 Instructions: Language of the Computer 1 Procedures A major program structuring mechanism Calling & returning from a procedure requires a protocol. The protocol is a sequence
2B 52 AB CA 3E A1 +29 A B C. CS120 Fall 2018 Final Prep and super secret quiz 9
 S2 Fall 28 Final Prep and super secret quiz 9 ) onvert 8-bit (2-digit) 2 s complement hex values: 4-29 inary: Hex: x29 2) onvert 8-bit 2 s complement hex to decimal: x3 inary: xe5 Decimal: 58 Note 3*6+
S2 Fall 28 Final Prep and super secret quiz 9 ) onvert 8-bit (2-digit) 2 s complement hex values: 4-29 inary: Hex: x29 2) onvert 8-bit 2 s complement hex to decimal: x3 inary: xe5 Decimal: 58 Note 3*6+
CSE 378 Final 3/18/10
 Name There are 10 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. Copies of the MIPS reference card ( green
Name There are 10 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. Copies of the MIPS reference card ( green
Final Exam Spring 2017
 COE 3 / ICS 233 Computer Organization Final Exam Spring 27 Friday, May 9, 27 7:3 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
COE 3 / ICS 233 Computer Organization Final Exam Spring 27 Friday, May 9, 27 7:3 AM Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
Stored Program Concept. Instructions: Characteristics of Instruction Set. Architecture Specification. Example of multiple operands
 Stored Program Concept Instructions: Instructions are bits Programs are stored in memory to be read or written just like data Processor Memory memory for data, programs, compilers, editors, etc. Fetch
Stored Program Concept Instructions: Instructions are bits Programs are stored in memory to be read or written just like data Processor Memory memory for data, programs, compilers, editors, etc. Fetch
CS31001 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE. Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, CSE, IIT Kharagpur. Instructions and Addressing
 CS31001 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, CSE, IIT Kharagpur Instructions and Addressing 1 ISA vs. Microarchitecture An ISA or Instruction Set Architecture describes the aspects
CS31001 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND ARCHITECTURE Debdeep Mukhopadhyay, CSE, IIT Kharagpur Instructions and Addressing 1 ISA vs. Microarchitecture An ISA or Instruction Set Architecture describes the aspects
The University of Alabama in Huntsville Electrical & Computer Engineering Department CPE Test II November 14, 2000
 The University of Alabama in Huntsville Electrical & Computer Engineering Department CPE 513 01 Test II November 14, 2000 Name: 1. (5 points) For an eight-stage pipeline, how many cycles does it take to
The University of Alabama in Huntsville Electrical & Computer Engineering Department CPE 513 01 Test II November 14, 2000 Name: 1. (5 points) For an eight-stage pipeline, how many cycles does it take to
CS 341l Fall 2008 Test #2
 CS 341l all 2008 Test #2 Name: Key CS 341l, test #2. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible while still answering
CS 341l all 2008 Test #2 Name: Key CS 341l, test #2. 100 points total, number of points each question is worth is indicated in parentheses. Answer all questions. Be as concise as possible while still answering
CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015
 CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015 Name: Rules and Hints The MIPS cheat sheet and datapath diagram are attached at the end of this exam for your reference. You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front
CS 351 Exam 2 Mon. 11/2/2015 Name: Rules and Hints The MIPS cheat sheet and datapath diagram are attached at the end of this exam for your reference. You may use one handwritten 8.5 11 cheat sheet (front
CS305, Computer Architecture, End Sem, Sat 21/11/09, 2:30 05:30pm, Max marks: 45
 CS305, Computer Architecture, End Sem, Sat 21/11/09, 2:30 05:30pm, Max marks: 45 Declaration (write by hand and sign): I hereby declare that I hold copying as an act as shameful as stealing, or bribery,
CS305, Computer Architecture, End Sem, Sat 21/11/09, 2:30 05:30pm, Max marks: 45 Declaration (write by hand and sign): I hereby declare that I hold copying as an act as shameful as stealing, or bribery,
CS433 Midterm. Prof Josep Torrellas. October 16, Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes
 CS433 Midterm Prof Josep Torrellas October 16, 2014 Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes examination. 2. The Exam has 4 Questions. Please budget your
CS433 Midterm Prof Josep Torrellas October 16, 2014 Time: 1 hour + 15 minutes Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This is a closed-book, closed-notes examination. 2. The Exam has 4 Questions. Please budget your
Final Exam Fall 2007
 ICS 233 - Computer Architecture & Assembly Language Final Exam Fall 2007 Wednesday, January 23, 2007 7:30 am 10:00 am Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd
ICS 233 - Computer Architecture & Assembly Language Final Exam Fall 2007 Wednesday, January 23, 2007 7:30 am 10:00 am Computer Engineering Department College of Computer Sciences & Engineering King Fahd
BITS, PILANI -DUBAI. International Academic City, Dubai BE (Hans) CS III Year -2nd Sem
 BITS, PILANI -DUBAI International Academic City, Dubai BE (Hans) CS III Year -2nd Sem ADVANCED C:OMPUTER ORGANISATION -CS UC 342 COMPREHENSIVE EXAM (Closed book) Date: 01 June 2008 Time: 3 hrs Max Marks:
BITS, PILANI -DUBAI International Academic City, Dubai BE (Hans) CS III Year -2nd Sem ADVANCED C:OMPUTER ORGANISATION -CS UC 342 COMPREHENSIVE EXAM (Closed book) Date: 01 June 2008 Time: 3 hrs Max Marks:
4. What is the average CPI of a 1.4 GHz machine that executes 12.5 million instructions in 12 seconds?
 Chapter 4: Assessing and Understanding Performance 1. Define response (execution) time. 2. Define throughput. 3. Describe why using the clock rate of a processor is a bad way to measure performance. Provide
Chapter 4: Assessing and Understanding Performance 1. Define response (execution) time. 2. Define throughput. 3. Describe why using the clock rate of a processor is a bad way to measure performance. Provide
LECTURE 10. Pipelining: Advanced ILP
 LECTURE 10 Pipelining: Advanced ILP EXCEPTIONS An exception, or interrupt, is an event other than regular transfers of control (branches, jumps, calls, returns) that changes the normal flow of instruction
LECTURE 10 Pipelining: Advanced ILP EXCEPTIONS An exception, or interrupt, is an event other than regular transfers of control (branches, jumps, calls, returns) that changes the normal flow of instruction
University of California College of Engineering Computer Science Division -EECS. CS 152 Midterm I
 Name: University of California College of Engineering Computer Science Division -EECS Fall 996 D.E. Culler CS 52 Midterm I Your Name: ID Number: Discussion Section: You may bring one double-sided pages
Name: University of California College of Engineering Computer Science Division -EECS Fall 996 D.E. Culler CS 52 Midterm I Your Name: ID Number: Discussion Section: You may bring one double-sided pages
CENG3420 Lecture 03 Review
 CENG3420 Lecture 03 Review Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk 2017 Spring 1 / 38 CISC vs. RISC Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) Lots of instructions of variable size, very memory optimal, typically less
CENG3420 Lecture 03 Review Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk 2017 Spring 1 / 38 CISC vs. RISC Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) Lots of instructions of variable size, very memory optimal, typically less
Binvert Operation (add, and, or) M U X
 Exercises 5 - IPS datapath and control Questions 1. In the circuit of the AL back in lecture 4, we included an adder, an AND gate, and an OR gate. A multiplexor was used to select one of these three values.
Exercises 5 - IPS datapath and control Questions 1. In the circuit of the AL back in lecture 4, we included an adder, an AND gate, and an OR gate. A multiplexor was used to select one of these three values.
Stored Program Concept. Instructions: Characteristics of Instruction Set. Architecture Specification. Example of multiple operands
 Stored Program Concept nstructions: nstructions are bits Programs are stored in memory to be read or written just like data Processor Memory memory for data, programs, compilers, editors, etc. Fetch &
Stored Program Concept nstructions: nstructions are bits Programs are stored in memory to be read or written just like data Processor Memory memory for data, programs, compilers, editors, etc. Fetch &
For More Practice FMP
 FMP 5.13-1 Single Cycle Datapaths with Floating Point 5.4 [5] < 5.4> Suppose we have a floating-point unit that requires 400 ps for a floating-point add and 600 ps for a floating-point multiply, not including
FMP 5.13-1 Single Cycle Datapaths with Floating Point 5.4 [5] < 5.4> Suppose we have a floating-point unit that requires 400 ps for a floating-point add and 600 ps for a floating-point multiply, not including
Winter 2002 FINAL EXAMINATION
 University of Calgary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ENCM 369: Computer Organization Instructors: Dr. S. A. Norman (L01) and Dr. S. Yanushkevich (L02) Note for Winter 2005 students Winter
University of Calgary Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ENCM 369: Computer Organization Instructors: Dr. S. A. Norman (L01) and Dr. S. Yanushkevich (L02) Note for Winter 2005 students Winter
CS 251, Winter 2019, Assignment % of course mark
 CS 251, Winter 2019, Assignment 5.1.1 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 27th, 5:30PM Lates accepted until 1:00pm March 28th with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
CS 251, Winter 2019, Assignment 5.1.1 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 27th, 5:30PM Lates accepted until 1:00pm March 28th with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
CSE 378 Midterm 2/12/10 Sample Solution
 Question 1. (6 points) (a) Rewrite the instruction sub $v0,$t8,$a2 using absolute register numbers instead of symbolic names (i.e., if the instruction contained $at, you would rewrite that as $1.) sub
Question 1. (6 points) (a) Rewrite the instruction sub $v0,$t8,$a2 using absolute register numbers instead of symbolic names (i.e., if the instruction contained $at, you would rewrite that as $1.) sub
Thomas Polzer Institut für Technische Informatik
 Thomas Polzer tpolzer@ecs.tuwien.ac.at Institut für Technische Informatik Branch to a labeled instruction if a condition is true Otherwise, continue sequentially beq rs, rt, L1 if (rs == rt) branch to
Thomas Polzer tpolzer@ecs.tuwien.ac.at Institut für Technische Informatik Branch to a labeled instruction if a condition is true Otherwise, continue sequentially beq rs, rt, L1 if (rs == rt) branch to
Control Instructions. Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing. Thursday, 26 September Summary
 Control Instructions Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Thursday, 26 September 2013 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Control Instructions Computer Organization Architectures for Embedded Computing Thursday, 26 September 2013 Many slides adapted from: Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 4th Edition,
Control Instructions
 Control Instructions Tuesday 22 September 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Instruction Set
Control Instructions Tuesday 22 September 15 Many slides adapted from: and Design, Patterson & Hennessy 5th Edition, 2014, MK and from Prof. Mary Jane Irwin, PSU Summary Previous Class Instruction Set
Chapter 3 MIPS Assembly Language. Ó1998 Morgan Kaufmann Publishers 1
 Chapter 3 MIPS Assembly Language Ó1998 Morgan Kaufmann Publishers 1 Instructions: Language of the Machine More primitive than higher level languages e.g., no sophisticated control flow Very restrictive
Chapter 3 MIPS Assembly Language Ó1998 Morgan Kaufmann Publishers 1 Instructions: Language of the Machine More primitive than higher level languages e.g., no sophisticated control flow Very restrictive
ECE 2035 A Programming Hw/Sw Systems Fall problems, 8 pages Final Exam 8 December 2014
 Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Instructions: This is a closed book, closed note exam. Calculators are not permitted. If you have a question, raise your hand and I will come to you. Please work the exam in pencil and do not separate
Faculty of Science FINAL EXAMINATION
 Faculty of Science FINAL EXAMINATION COMPUTER SCIENCE COMP 273 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEMS Examiner: Prof. Michael Langer April 18, 2012 Associate Examiner: Mr. Joseph Vybihal 2 P.M. 5 P.M. STUDENT
Faculty of Science FINAL EXAMINATION COMPUTER SCIENCE COMP 273 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEMS Examiner: Prof. Michael Langer April 18, 2012 Associate Examiner: Mr. Joseph Vybihal 2 P.M. 5 P.M. STUDENT
1 5. Addressing Modes COMP2611 Fall 2015 Instruction: Language of the Computer
 1 5. Addressing Modes MIPS Addressing Modes 2 Addressing takes care of where to find data instruction We have seen, so far three addressing modes of MIPS (to find data): 1. Immediate addressing: provides
1 5. Addressing Modes MIPS Addressing Modes 2 Addressing takes care of where to find data instruction We have seen, so far three addressing modes of MIPS (to find data): 1. Immediate addressing: provides
 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. Objectives: Using the Logisim simulator Designing and testing a Pipelined 16-bit
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. Objectives: Using the Logisim simulator Designing and testing a Pipelined 16-bit
Part II Instruction-Set Architecture. Jan Computer Architecture, Instruction-Set Architecture Slide 1
 Part II Instruction-Set Architecture Jan. 211 Computer Architecture, Instruction-Set Architecture Slide 1 Short review of the previous lecture Performance = 1/(Execution time) = Clock rate / (Average CPI
Part II Instruction-Set Architecture Jan. 211 Computer Architecture, Instruction-Set Architecture Slide 1 Short review of the previous lecture Performance = 1/(Execution time) = Clock rate / (Average CPI
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering
 ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #3 Spring 2015 Use the MIPS assembly instructions listed below to solve the following problems. arithmetic add add sub subtract addi add
ECE 30 Introduction to Computer Engineering Study Problems, Set #3 Spring 2015 Use the MIPS assembly instructions listed below to solve the following problems. arithmetic add add sub subtract addi add
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Machine Organization & Assembly Language
 Name: CSE 378 Winter 29 Machine Organization & Assembly Language Midterm Exam Solution your answers on these pages. itional pages may be attached (with staple) if necessary. Please ensure that your answers
Name: CSE 378 Winter 29 Machine Organization & Assembly Language Midterm Exam Solution your answers on these pages. itional pages may be attached (with staple) if necessary. Please ensure that your answers
ECE 313 Computer Organization EXAM 2 November 11, 2000
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 50 minutes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. ALU Design / Logic Operations 20 Points The subset of
This exam is open book and open notes. You have 50 minutes. Credit for problems requiring calculation will be given only if you show your work. 1. ALU Design / Logic Operations 20 Points The subset of
Static, multiple-issue (superscaler) pipelines
 Static, multiple-issue (superscaler) pipelines Start more than one instruction in the same cycle Instruction Register file EX + MEM + WB PC Instruction Register file EX + MEM + WB 79 A static two-issue
Static, multiple-issue (superscaler) pipelines Start more than one instruction in the same cycle Instruction Register file EX + MEM + WB PC Instruction Register file EX + MEM + WB 79 A static two-issue
Instructions: MIPS ISA. Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer 1
 Instructions: MIPS ISA Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer 1 PH Chapter 2 Pt A Instructions: MIPS ISA Based on Text: Patterson Henessey Publisher: Morgan Kaufmann Edited by Y.K. Malaiya for
Instructions: MIPS ISA Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer 1 PH Chapter 2 Pt A Instructions: MIPS ISA Based on Text: Patterson Henessey Publisher: Morgan Kaufmann Edited by Y.K. Malaiya for
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012
 CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
CS 351 Exam 2, Fall 2012 Your name: Rules You may use one handwritten 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet (front and back). This is the only resource you may consult during this exam. Include explanations and comments
Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam
 Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam NAME: STUDENT NUMBER 1. Consider a computer system with 64Kbytes main memory and 256bytes cache. If we assume the cache line size is
Computer Organization and Architecture (CSCI-365) Sample Final Exam NAME: STUDENT NUMBER 1. Consider a computer system with 64Kbytes main memory and 256bytes cache. If we assume the cache line size is
CS 2506 Computer Organization II
 Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
Instructions: Print your name in the space provided below. This examination is closed book and closed notes, aside from the permitted one-page formula sheet. No calculators or other computing devices may
CSE 378 Midterm Sample Solution 2/11/11
 Question 1. (9 points). Suppose we have the following MIPS instructions stored in memory starting at location 0x2400. 2400: add $v0,$t1,$t3 2404: loop: sll $t3,$a2,12 2408: or $s2,$t3,$a1 240c: bne $s2,$t8,loop
Question 1. (9 points). Suppose we have the following MIPS instructions stored in memory starting at location 0x2400. 2400: add $v0,$t1,$t3 2404: loop: sll $t3,$a2,12 2408: or $s2,$t3,$a1 240c: bne $s2,$t8,loop
CSE 141 Computer Architecture Spring Lecture 3 Instruction Set Architecute. Course Schedule. Announcements
 CSE141: Introduction to Computer Architecture CSE 141 Computer Architecture Spring 2005 Lecture 3 Instruction Set Architecute Pramod V. Argade April 4, 2005 Instructor: TAs: Pramod V. Argade (p2argade@cs.ucsd.edu)
CSE141: Introduction to Computer Architecture CSE 141 Computer Architecture Spring 2005 Lecture 3 Instruction Set Architecute Pramod V. Argade April 4, 2005 Instructor: TAs: Pramod V. Argade (p2argade@cs.ucsd.edu)
Chapter 2. Computer Abstractions and Technology. Lesson 4: MIPS (cont )
 Chapter 2 Computer Abstractions and Technology Lesson 4: MIPS (cont ) Logical Operations Instructions for bitwise manipulation Operation C Java MIPS Shift left >>> srl Bitwise
Chapter 2 Computer Abstractions and Technology Lesson 4: MIPS (cont ) Logical Operations Instructions for bitwise manipulation Operation C Java MIPS Shift left >>> srl Bitwise
Branch Addressing. Jump Addressing. Target Addressing Example. The University of Adelaide, School of Computer Science 28 September 2015
 Branch Addressing Branch instructions specify Opcode, two registers, target address Most branch targets are near branch Forward or backward op rs rt constant or address 6 bits 5 bits 5 bits 16 bits PC-relative
Branch Addressing Branch instructions specify Opcode, two registers, target address Most branch targets are near branch Forward or backward op rs rt constant or address 6 bits 5 bits 5 bits 16 bits PC-relative
Chapter 2. Instructions: Language of the Computer. Adapted by Paulo Lopes
 Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer Adapted by Paulo Lopes Instruction Set The repertoire of instructions of a computer Different computers have different instruction sets But with many aspects
Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer Adapted by Paulo Lopes Instruction Set The repertoire of instructions of a computer Different computers have different instruction sets But with many aspects
CS 251, Winter 2018, Assignment % of course mark
 CS 251, Winter 2018, Assignment 5.0.4 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 21st, 4:30PM Lates accepted until 10:00am March 22nd with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
CS 251, Winter 2018, Assignment 5.0.4 3% of course mark Due Wednesday, March 21st, 4:30PM Lates accepted until 10:00am March 22nd with a 15% penalty 1. (10 points) The code sequence below executes on a
ECE550 PRACTICE Final
 ECE550 PRACTICE Final This is a full length practice midterm exam. If you want to take it at exam pace, give yourself 175 minutes to take the entire test. Just like the real exam, each question has a point
ECE550 PRACTICE Final This is a full length practice midterm exam. If you want to take it at exam pace, give yourself 175 minutes to take the entire test. Just like the real exam, each question has a point
Machine Language Instructions Introduction. Instructions Words of a language understood by machine. Instruction set Vocabulary of the machine
 Machine Language Instructions Introduction Instructions Words of a language understood by machine Instruction set Vocabulary of the machine Current goal: to relate a high level language to instruction
Machine Language Instructions Introduction Instructions Words of a language understood by machine Instruction set Vocabulary of the machine Current goal: to relate a high level language to instruction
Introduction to MIPS Processor
 Introduction to MIPS Processor The processor we will be considering in this tutorial is the MIPS processor. The MIPS processor, designed in 1984 by researchers at Stanford University, is a RISC (Reduced
Introduction to MIPS Processor The processor we will be considering in this tutorial is the MIPS processor. The MIPS processor, designed in 1984 by researchers at Stanford University, is a RISC (Reduced
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer Fall 2005 Department of Computer Science Kent State University Assembly Language Encodes machine instructions using symbols and numbers
Computer Architecture Chapter 2 Instructions: Language of the Computer Fall 2005 Department of Computer Science Kent State University Assembly Language Encodes machine instructions using symbols and numbers
CS 61c: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture
 MIPS Functions July 1, 2014 Review I RISC Design Principles Smaller is faster: 32 registers, fewer instructions Keep it simple: rigid syntax, fixed instruction length MIPS Registers: $s0-$s7,$t0-$t9, $0
MIPS Functions July 1, 2014 Review I RISC Design Principles Smaller is faster: 32 registers, fewer instructions Keep it simple: rigid syntax, fixed instruction length MIPS Registers: $s0-$s7,$t0-$t9, $0
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : CS6303 / COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE SEM / YEAR : VI / III year B.E. Unit I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS Part A Q.No Questions BT Level
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : CS6303 / COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE SEM / YEAR : VI / III year B.E. Unit I OVERVIEW AND INSTRUCTIONS Part A Q.No Questions BT Level
Pipelining and Caching. CS230 Tutorial 09
 Pipelining and Caching CS230 Tutorial 09 Pipelining Hazards Data hazard: What happens when one instruction needs something that isn t ready? Example: add $3, $1, $2 add $5, $3, $4 This is solved by forwarding
Pipelining and Caching CS230 Tutorial 09 Pipelining Hazards Data hazard: What happens when one instruction needs something that isn t ready? Example: add $3, $1, $2 add $5, $3, $4 This is solved by forwarding
ECE 341 Final Exam Solution
 ECE 341 Final Exam Solution Time allowed: 110 minutes Total Points: 100 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE.
ECE 341 Final Exam Solution Time allowed: 110 minutes Total Points: 100 Points Scored: Name: Problem No. 1 (10 points) For each of the following statements, indicate whether the statement is TRUE or FALSE.
Programming the processor
 CSC258 Week 9 Logistics This week: Lab 7 is the last Logisim DE2 lab. Next week: Lab 8 will be assembly. For assembly labs you can work individually or in pairs. No matter how you do it, the important
CSC258 Week 9 Logistics This week: Lab 7 is the last Logisim DE2 lab. Next week: Lab 8 will be assembly. For assembly labs you can work individually or in pairs. No matter how you do it, the important
CS3350B Computer Architecture MIPS Introduction
 CS3350B Computer Architecture MIPS Introduction Marc Moreno Maza http://www.csd.uwo.ca/~moreno/cs3350_moreno/index.html Department of Computer Science University of Western Ontario, Canada Thursday January
CS3350B Computer Architecture MIPS Introduction Marc Moreno Maza http://www.csd.uwo.ca/~moreno/cs3350_moreno/index.html Department of Computer Science University of Western Ontario, Canada Thursday January
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 2014
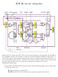 ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
ECE 30, Lab #8 Spring 20 Shown above is a multi-cycle CPU. There are six special registers in this datapath: PC, IR, MDR, A, B, and ALUOut. Of these, PC and IR are enabled to change when PCWr and IRWr
Exam in Computer Architecture
 Exam in Computer Architecture Justin Pearson 2002-03-07 Cover Sheet Problem no. Solution provided Max Your points 1 1 2 6 3 14 4 9 5 13 6 11 7 10 Total: 64 Name :...................................................
Exam in Computer Architecture Justin Pearson 2002-03-07 Cover Sheet Problem no. Solution provided Max Your points 1 1 2 6 3 14 4 9 5 13 6 11 7 10 Total: 64 Name :...................................................
Course Administration
 Fall 2018 EE 3613: Computer Organization Chapter 2: Instruction Set Architecture Introduction 4/4 Avinash Karanth Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701
Fall 2018 EE 3613: Computer Organization Chapter 2: Instruction Set Architecture Introduction 4/4 Avinash Karanth Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701
ECE 313 Computer Organization FINAL EXAM December 14, This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours.
 This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-4 refer to a proposed MIPS instruction lwu (load word - update) which implements update addressing an addressing mode that is used in
This exam is open book and open notes. You have 2 hours. Problems 1-4 refer to a proposed MIPS instruction lwu (load word - update) which implements update addressing an addressing mode that is used in
Midterm #2 Solutions April 23, 1997
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Sp97 D.K. Jeong Midterm #2 Solutions
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Sp97 D.K. Jeong Midterm #2 Solutions
CS64 Week 5 Lecture 1. Kyle Dewey
 CS64 Week 5 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview More branches in MIPS Memory in MIPS MIPS Calling Convention More Branches in MIPS else_if.asm nested_if.asm nested_else_if.asm Memory in MIPS Accessing Memory
CS64 Week 5 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview More branches in MIPS Memory in MIPS MIPS Calling Convention More Branches in MIPS else_if.asm nested_if.asm nested_else_if.asm Memory in MIPS Accessing Memory
1. Truthiness /8. 2. Branch prediction /5. 3. Choices, choices /6. 5. Pipeline diagrams / Multi-cycle datapath performance /11
 The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS 370 Introduction to Computer Architecture Midterm Exam 2 ANSWER KEY November 23 rd, 2010 Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID
The University of Michigan - Department of EECS EECS 370 Introduction to Computer Architecture Midterm Exam 2 ANSWER KEY November 23 rd, 2010 Name: University of Michigan uniqname: (NOT your student ID
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 03: Instruction Set Architecture Design
 ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 03: Instruction Set Architecture Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2014 Sources: Computer
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 03: Instruction Set Architecture Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu School of Engineering Brown University Spring 2014 Sources: Computer
Chapter 4. The Processor. Computer Architecture and IC Design Lab
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors CPI Clock Cycle Time Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS
Cache Organizations for Multi-cores
 Lecture 26: Recap Announcements: Assgn 9 (and earlier assignments) will be ready for pick-up from the CS front office later this week Office hours: all day next Tuesday Final exam: Wednesday 13 th, 7:50-10am,
Lecture 26: Recap Announcements: Assgn 9 (and earlier assignments) will be ready for pick-up from the CS front office later this week Office hours: all day next Tuesday Final exam: Wednesday 13 th, 7:50-10am,
ECE 2035 Programming HW/SW Systems Fall problems, 6 pages Exam One 22 September Your Name (please print clearly) Signed.
 Your Name (please print clearly) This exam will be conducted according to the Georgia Tech Honor Code. I pledge to neither give nor receive unauthorized assistance on this exam and to abide by all provisions
Your Name (please print clearly) This exam will be conducted according to the Georgia Tech Honor Code. I pledge to neither give nor receive unauthorized assistance on this exam and to abide by all provisions
